Types of numbers | Rational numbers | Irrational numbers
Know all 11 types of numbers in-depth along with examples. These are always asked in school exams, competitive exams, and interviews.
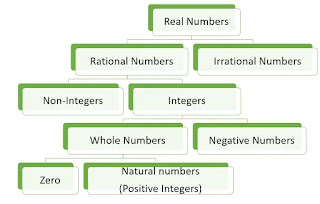
Types of Numbers:
- Real Number
- Rational Number
- Irrational Number
- Integers
- Whole Number
- Natural Number
- Prime Number
- Composite Number
- Even Number
- Odd number
- Complete Number
 |
| Type of numbers |
Real Number:
Real number is any number (Positive, Negative
or Zero) that includes all the rational and irrational numbers.
Example: 1, 2.2684654, π, 8/3 etc
A real number always can be found on the number line. These
are the numbers we use in real-world applications.
Rational Number:
A number which can be written in the form
of P/q, where both P and q are integers and q is not equal to zero.
- All the fractions are rational numbers. For example 3/8
- Integers are rational numbers. For example, 6 is a rational number because it can be written as 6/1
- All the decimal numbers terminated after a few decimal points are rational numbers. Example 2.15, 216.3698
- All the decimal numbers which do not terminate but its digits are repeating in nature are also rational numbers.
- For example - 3.333333333.......... And 0.714285714285……….
- In 3.3333333, 3 is not terminated but it gets repeated, so it is a rational number. It can be written as 10/3.
- In 0.714285714285, 714285 continuously gets repeated so it is also a rational number and it can be written as 5/7.
Irrational numbers:
These numbers can not be written in the
form of p/q.
Π is an irrational number, where Π = 3.141592654…….
Π is irrational because neither it is terminating nor repeating in
nature.
Integers:
An integer is a number that can be written without
a fractional component. In other words, an integer has denominator equal to 1.
Example: -20, 0, 516
Whole Numbers:
These are the numbers which contain zero and
positive integers.
Example: 0, 13, 150
Natural numbers:
Positive
integers are known as a natural number. Zero is not a natural number. So if we
remove zero from the list of whole numbers we get the natural number.
Example: 1, 1234, 23246
Prime numbers:
A prime number is a number is only divisible by 1 and
itself.
Example: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11
- 1 is not a prime number
- 2 is the smallest prime number
- Also, 2 is only even prime number
Composite numbers:
All the positive integers other than
prime numbers are composite numbers.
Example: 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12
- 1 is neither prime nor composite.
Even numbers:
Those numbers which are divisible by 2 are
even numbers, in other words, the numbers whose unit digit is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8
are even numbers.
Example: 28, 226
Odd numbers:
Those numbers which are not divisible by 2 are
called odd numbers, in other words, the numbers whose unit digit is 1, 3, 5, 7,
9 are called odd numbers.
Example: 21, 233
Complete number:
A positive number is said to be complete if
the sum of all positive divisors of the number is equal to the twice of the
number itself.
Example: 6, 28
- Divisor of 6 are 1, 2, 3 and 6
1 + 2 + 3 + 6 = 12, which is the twice of 6, So 6 is a
complete number
- Divisor of 28 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 28
1 + 2 + 4 + 7 + 14 + 28 = 56, which is twice of 28 so 56 is
a complete number.
If you like this article, Please like, share and follow my blog
If you have any doubt you can ask on comment section................
Types of numbers | Rational numbers | Irrational numbers
 Reviewed by goodinfo
on
October 21, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by goodinfo
on
October 21, 2019
Rating:
 Reviewed by goodinfo
on
October 21, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by goodinfo
on
October 21, 2019
Rating:







very good explanation sir.....
ReplyDelete